Cold Forging Machines: Revolutionizing Modern Manufacturing
Cold forging, also known as cold forming, is a manufacturing process that shapes metal at or near room temperature using high pressure. Cold forging machines are specialized equipment designed to perform this process efficiently, producing high-strength, precision components for various industries. Unlike hot forging, which requires heating metal to high temperatures, cold forging offers advantages such as improved material strength, better surface finish, and reduced waste. This article explores the principles, types, applications, and benefits of cold forging machines in today's industrial landscape.
How Cold Forging Machines Work
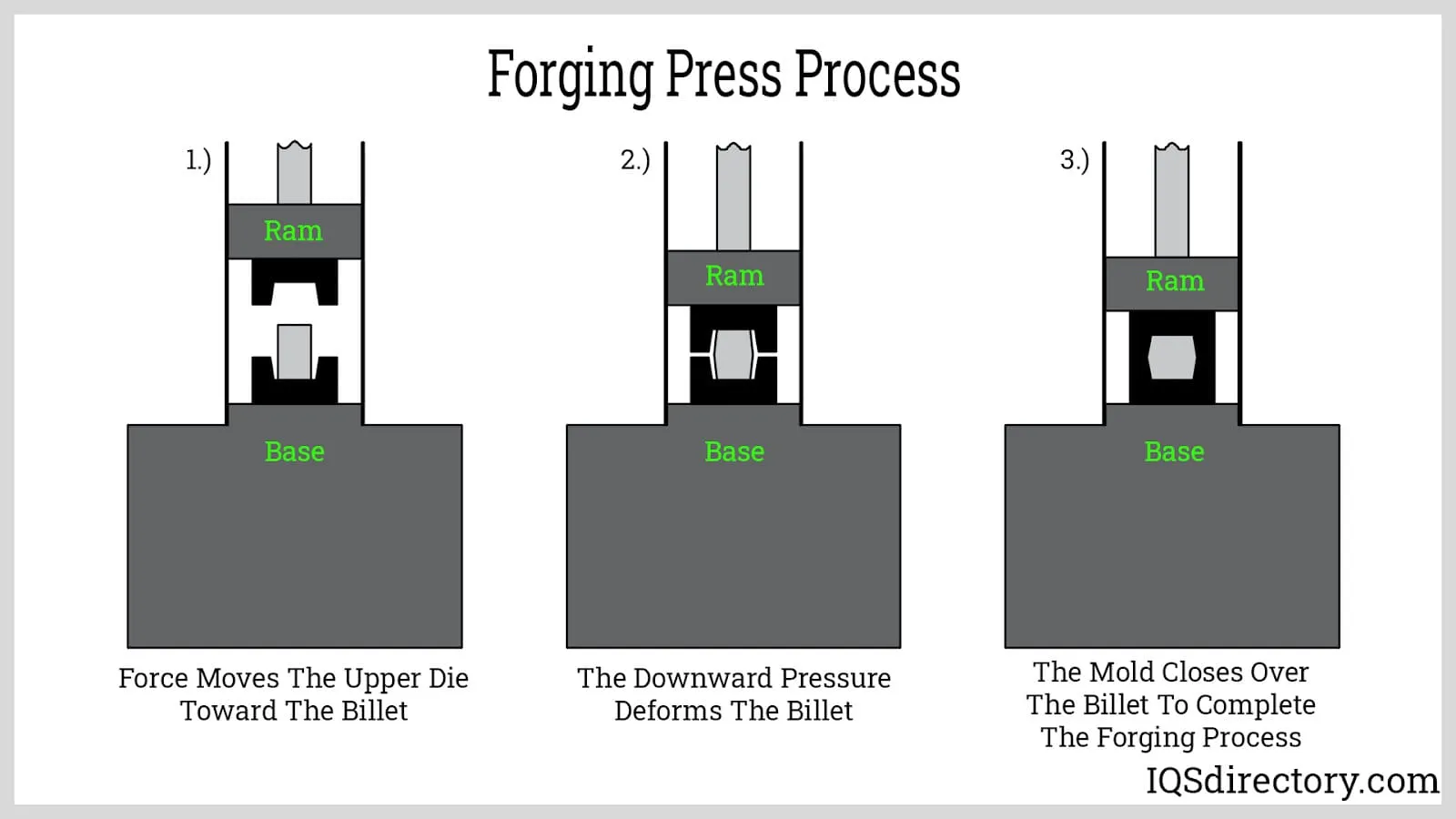
Cold forging machines operate by applying compressive forces to metal blanks, causing plastic deformation without heating. The process typically involves several stages, including heading, extrusion, and piercing. The machine uses dies and punches to shape the metal into the desired form. The absence of heat reduces oxidation and scaling, resulting in components with excellent dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
Key Components of a Cold Forging Machine
A typical cold forging machine consists of a frame, a ram, dies, a feeding system, and a control unit. The frame provides structural support, while the ram delivers the force needed for deformation. Dies define the shape of the final product, and the feeding system ensures precise material placement. Modern machines are equipped with CNC systems for automation and precision.
Types of Cold Forging Machines
Cold forging machines are categorized based on their mechanism and application. The main types include mechanical presses, hydraulic presses, and multi-station formers.
Mechanical Cold Forging Presses
Mechanical presses use a motor-driven crank mechanism to generate force. They are known for high speed and efficiency, making them suitable for mass production of small to medium-sized parts like bolts and screws.
Hydraulic Cold Forging Presses
Hydraulic presses use fluid pressure to generate force, offering greater control over speed and pressure. They are ideal for forming larger or more complex parts that require variable force application.
Multi-Station Cold Forging Machines
These machines feature multiple dies and transfer systems, allowing sequential forming operations in a single cycle. They are used for producing complex components with high precision and reduced cycle times.
| Machine Type | Force Mechanism | Typical Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Press | Crank-driven | Bolts, screws, small fasteners | High speed, low cost per part |
| Hydraulic Press | Fluid pressure | Large or complex parts | Precise control, versatility |
| Multi-Station Former | Transfer system | Complex components (e.g., gears) | High productivity, minimal handling |
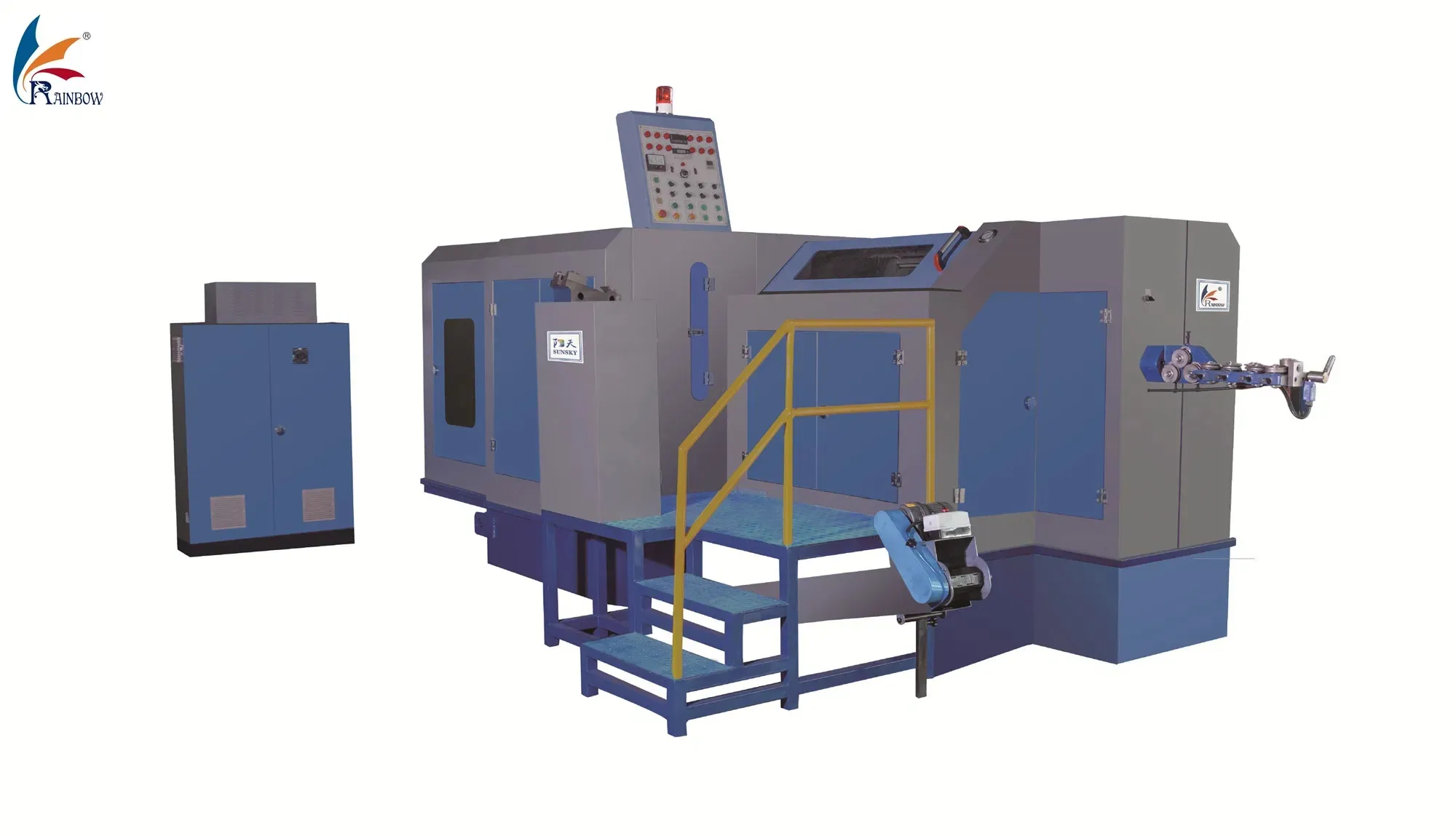

Applications of Cold Forging Machines
Cold forging is widely used in industries requiring high-strength, durable components. Key sectors include automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics.
Automotive Industry
Cold forging produces critical parts such as shafts, gears, and engine components. The process enhances strength and fatigue resistance, contributing to vehicle safety and performance.
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace, cold-forged parts meet stringent standards for reliability and weight savings. Applications include landing gear components and fasteners.
Consumer Electronics
Small, precision parts like connectors and housings are efficiently manufactured using cold forging, ensuring durability and consistent quality.
Benefits of Cold Forging Machines
Cold forging offers numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods:
- Material Savings: Minimal scrap due to near-net-shape forming.
- Enhanced Strength: Work hardening improves mechanical properties.
- High Productivity: Rapid cycle times enable mass production.
- Superior Surface Finish: Reduced need for secondary machining.

Future Trends in Cold Forging Technology
Advancements in automation, IoT, and material science are shaping the future of cold forging. Smart machines with real-time monitoring and AI-driven optimization are increasing efficiency and reducing downtime. Additionally, the development of new alloys expands the applications of cold forging in emerging industries like renewable energy.
| Trend | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Automation & Robotics | Higher precision, reduced labor costs | Robotic part handling systems |
| IoT Integration | Predictive maintenance, data analytics | Real-time performance monitoring |
| Sustainable Manufacturing | Energy efficiency, waste reduction | Eco-friendly lubricants |
In conclusion, cold forging machines are indispensable in modern manufacturing, offering efficiency, precision, and sustainability. As technology evolves, their role in producing high-quality components will continue to grow.