Cold Heading Machines for Bolts: The Complete Guide
Cold heading machines represent one of the most significant advancements in modern industrial manufacturing, particularly in the production of bolts and fasteners. These sophisticated machines have transformed how manufacturers create high-quality, precision-engineered bolts for countless applications across various industries.
What Are Cold Heading Machines?
Cold heading machines, also known as cold formers or headers, are specialized industrial equipment designed to form metal parts at room temperature through a process called cold working. Unlike traditional machining methods that remove material, cold heading displaces and reforms metal using high pressure, resulting in minimal material waste and superior mechanical properties.
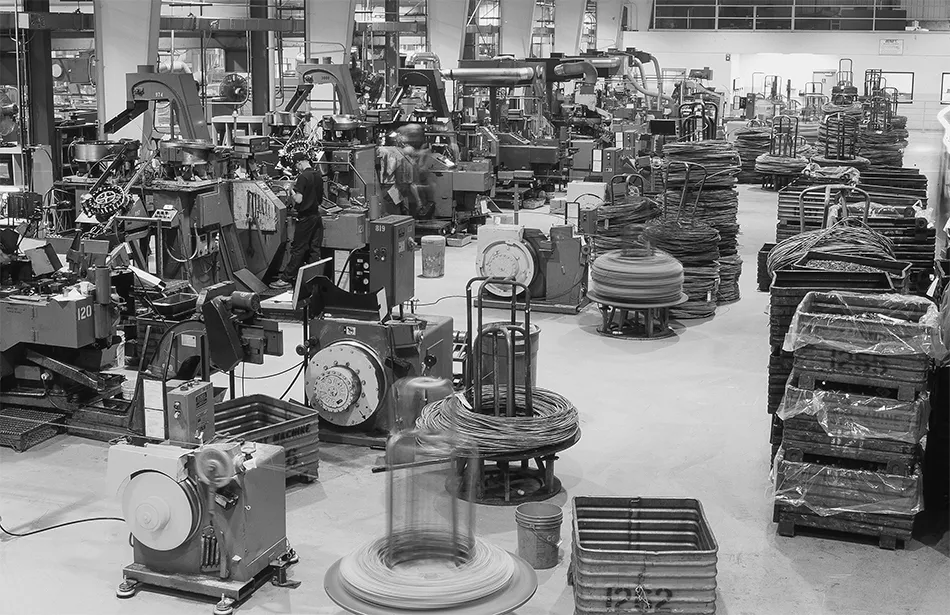

The Cold Heading Process Explained
Material Preparation
The process begins with wire rods, typically made from steel, stainless steel, or non-ferrous metals. These rods are drawn to precise diameters and cut into specific lengths called blanks or slugs.
Forming Operations
Cold heading involves several forming operations including:
- Upsetting: Increasing diameter by reducing length
- Extruding: Reducing diameter while maintaining volume
- Piercing: Creating internal features or holes
- Thread rolling: Forming threads through displacement
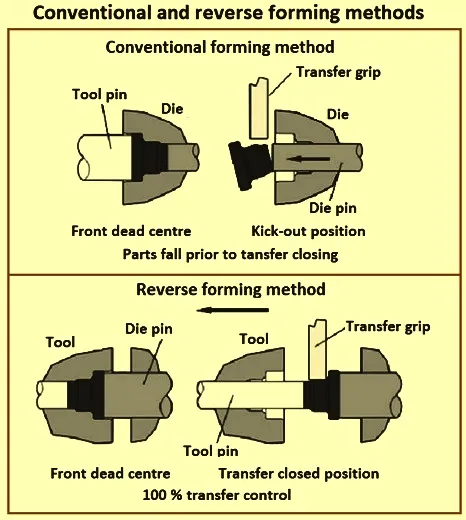
Types of Cold Heading Machines
| Machine Type | Stations | Production Capacity | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Stroke Headers | 1 | Up to 150 pieces/minute | Simple bolts, basic fasteners |
| Double-Stroke Headers | 2 | Up to 250 pieces/minute | Standard bolts, specialized fasteners |
| Multi-Station Headers | 3-5 | Up to 400 pieces/minute | Complex bolts, automotive fasteners |
| Progressive Headers | 5+ | Up to 600 pieces/minute | High-precision bolts, aerospace components |
Key Advantages of Cold Heading for Bolt Production
Material Efficiency
Cold heading achieves material utilization rates of 95-99%, significantly higher than traditional machining methods that typically waste 40-60% of material as chips.
Enhanced Mechanical Properties
The cold working process improves grain structure and creates continuous grain flow, resulting in bolts with superior strength, fatigue resistance, and durability.
High Production Rates
Modern cold heading machines can produce hundreds of bolts per minute, making them ideal for high-volume manufacturing requirements.

Technical Specifications and Capabilities
| Parameter | Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Bolt Diameter | M3 to M24 (0.118" to 0.945") | General purpose to heavy machinery |
| Bolt Length | 10mm to 200mm (0.4" to 7.9") | Various industrial applications |
| Production Speed | 50-600 pieces/minute | Mass production requirements |
| Material Compatibility | Steel, stainless steel, brass, aluminum | Multiple industry standards |
| Tolerance | ±0.05mm to ±0.1mm | Precision engineering applications |
Modern Features and Automation
Computer Numerical Control (CNC)
Modern cold heading machines incorporate CNC technology for precise control over forming operations, tool positioning, and production parameters.
Automated Quality Control
Integrated vision systems and sensors monitor dimensional accuracy, surface defects, and material consistency throughout the production process.
Tooling Advancements
Advanced tool materials including carbide and specialized coatings extend tool life and maintain consistent quality over extended production runs.
Industry Applications
Automotive Industry
Cold heading produces critical fasteners for engine components, chassis systems, and body assemblies with required strength and reliability standards.
Construction and Infrastructure
Structural bolts, anchor bolts, and specialized fasteners for building construction and civil engineering projects.
Aerospace and Defense
High-strength, precision bolts for aircraft assemblies, military equipment, and space applications.
Consumer Products
Fasteners for appliances, electronics, furniture, and general consumer goods manufacturing.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Proper maintenance including lubrication, tool inspection, and alignment checks ensures consistent performance and extends machine lifespan.
Operator Training
Skilled operators are essential for optimal machine performance, quality control, and troubleshooting.
Safety Protocols
Comprehensive safety measures including machine guarding, emergency stops, and proper personal protective equipment are mandatory.

Future Trends and Developments
Industry 4.0 Integration
Cold heading machines are increasingly incorporating IoT connectivity, data analytics, and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Sustainable Manufacturing
Energy-efficient designs, reduced material waste, and environmentally friendly lubricants are becoming standard features.
Advanced Materials Compatibility
Development of machines capable of processing high-strength alloys, composites, and specialized materials for emerging applications.
Conclusion
Cold heading machines for bolts represent the pinnacle of efficient, high-quality fastener manufacturing. Their ability to produce superior bolts with minimal material waste, combined with high production rates and advanced automation capabilities, makes them indispensable in modern industrial manufacturing. As technology continues to evolve, these machines will play an increasingly vital role in meeting the growing demand for precision fasteners across global industries.