Comprehensive Guide to Shearing Machine Operation and Applications
Shearing machines are essential industrial equipment used for cutting sheet metal and plate materials with precision and efficiency. These machines employ a straightforward yet powerful cutting mechanism that makes them indispensable in metal fabrication shops, manufacturing facilities, and construction industries worldwide.
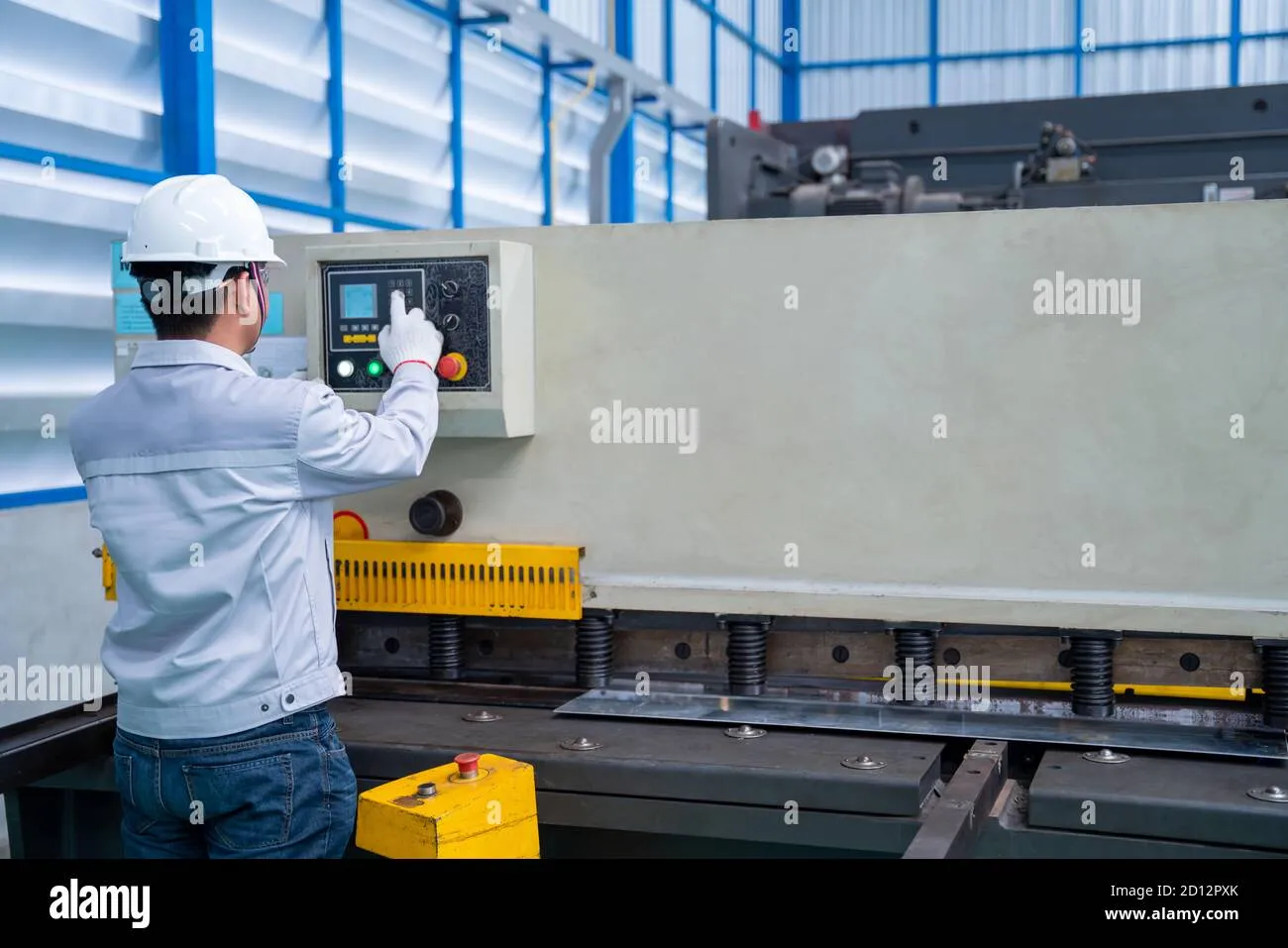

Working Principle of Shearing Machines
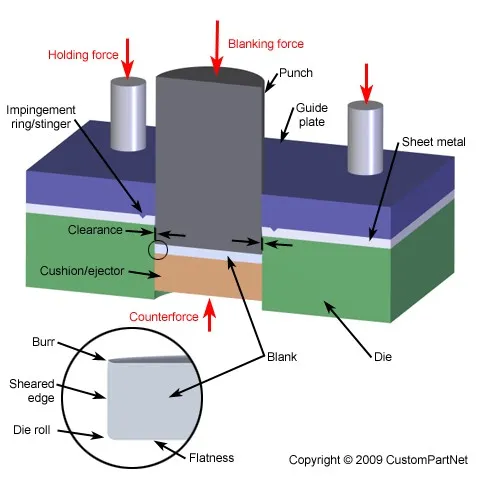
The fundamental working principle of shearing machines involves applying tremendous force to separate material along a straight line. This process occurs through the interaction of two primary components: the upper blade (moving blade) and the lower blade (stationary blade).
Basic Cutting Mechanism
When operational, the upper blade descends with significant force, pressing the material against the lower blade. The immense pressure causes the material to yield and fracture along the predetermined cutting line. This action creates a clean, straight cut without generating chips or significant material waste.
Force Application and Material Separation
The cutting force required depends on several factors including material thickness, tensile strength, and blade sharpness. Modern shearing machines utilize hydraulic or mechanical systems to generate the necessary cutting force, which can range from a few tons for thin sheets to hundreds of tons for thick plates.

Types of Shearing Machines
Shearing machines come in various configurations, each designed for specific applications and material types. Understanding these variations helps in selecting the appropriate machine for particular manufacturing requirements.
| Machine Type | Working Principle | Maximum Capacity | Primary Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Shears | Uses mechanical flywheel and clutch system | Up to 10mm thickness | High-speed production, thin to medium sheets | Fast operation, energy efficient, low maintenance |
| Hydraulic Shears | Hydraulic cylinders provide cutting force | Up to 50mm thickness | Heavy plates, variable thickness materials | Greater cutting force, adjustable stroke, overload protection |
| CNC Shears | Computer-controlled hydraulic or mechanical system | Varies by model | Precision cutting, complex shapes, high-volume production | Automated operation, high accuracy, repeatability |
| Guillotine Shears | Pivoting blade mechanism | Up to 25mm thickness | Straight cuts on plates and sheets | Simple design, reliable operation, cost-effective |
Key Components and Their Functions
Understanding the major components of shearing machines is crucial for proper operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Blade System
The blade system consists of upper and lower blades manufactured from high-carbon, high-chromium steel or tungsten carbide for durability and sharpness retention. Blade clearance—the gap between upper and lower blades—is critical for achieving clean cuts and varies based on material thickness.
Hold-down Mechanism
This component securely clamps the material during cutting operations, preventing movement that could cause inaccurate cuts or safety hazards. Modern machines feature hydraulic or pneumatic hold-down systems with adjustable pressure settings.
Back Gauge System
The back gauge provides precise positioning of the material for accurate cutting dimensions. Advanced models incorporate CNC-controlled back gauges that can be programmed for complex cutting sequences.

Operating Procedures and Safety Considerations
Proper operation of shearing machines requires adherence to established procedures and safety protocols to ensure both quality results and operator protection.
Standard Operating Sequence
The typical shearing operation follows a systematic sequence: material inspection → machine setup → blade clearance adjustment → back gauge positioning → material loading → clamping → cutting → unclamping → material removal. Each step must be performed meticulously to maintain cutting accuracy and operational safety.
Essential Safety Measures
Shearing machines present significant hazards including crushing points, sharp edges, and high-force operations. Critical safety measures include:
| Safety Feature | Purpose | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Two-hand Operation | Prevents accidental activation | Requires simultaneous pressing of two separate buttons |
| Light Curtains | Detects operator presence in danger zone | Automatically stops machine when beam is interrupted |
| Emergency Stop | Immediate machine shutdown | Large, easily accessible red button |
| Blade Guards | Prevents contact with sharp blades | Physical barriers around cutting area |
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance ensures consistent performance and extends the service life of shearing machines. A comprehensive maintenance program addresses both preventive and corrective aspects.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
Daily maintenance includes blade inspection, cleaning of cutting area, and lubrication of moving parts. Weekly tasks involve checking hydraulic systems, verifying safety devices, and inspecting electrical components. Monthly maintenance should include comprehensive blade sharpness assessment, alignment verification, and thorough system inspection.
Common Operational Issues
Typical problems encountered during shearing operations include burred edges (indicating dull blades or incorrect clearance), angular distortion (caused by uneven blade wear), and material dragging (resulting from insufficient hold-down pressure). Prompt identification and correction of these issues maintain cutting quality and prevent secondary problems.

Advanced Technologies in Modern Shearing
Recent technological advancements have significantly enhanced shearing machine capabilities, improving precision, efficiency, and operational safety.
CNC and Automation Integration
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems have revolutionized shearing operations by enabling automated back gauge positioning, angle programming, and complex cutting sequences. These systems reduce setup times, minimize human error, and increase production throughput.
Laser Measurement Systems
Integrated laser measurement systems project cutting lines onto the material, providing visual guidance for operators and ensuring accurate positioning. This technology significantly reduces material waste and improves first-cut accuracy.
Smart Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Modern shearing machines incorporate sensors and IoT connectivity to monitor performance parameters, track blade wear, and predict maintenance requirements. This proactive approach minimizes unplanned downtime and optimizes maintenance schedules.
Applications Across Industries
Shearing machines serve diverse industrial sectors, each with specific requirements and applications.
| Industry | Typical Materials | Common Applications | Special Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Mild steel, aluminum sheets | Body panels, chassis components | High precision, burr-free edges |
| Aerospace | Aluminum alloys, titanium | Structural components, skin panels | Strict tolerance control, material integrity |
| Construction | Structural steel, rebar | Beams, columns, reinforcement | Heavy-duty capacity, durability |
| Appliance Manufacturing | Stainless steel, coated sheets | Housings, brackets, panels | Surface finish preservation |
Shearing machines represent a cornerstone technology in modern manufacturing and metal fabrication. Their evolution from simple mechanical devices to sophisticated CNC-controlled systems demonstrates the ongoing innovation in industrial cutting technology. Understanding the working principles, operational procedures, maintenance requirements, and safety considerations enables manufacturers to maximize productivity while maintaining high quality standards and ensuring operator safety. As technology continues to advance, shearing machines will undoubtedly incorporate more intelligent features, further enhancing their capabilities and applications across diverse industrial sectors.