Powder Metal Compaction Press: The Core of Modern Manufacturing
Powder Metal Compaction Presses are specialized hydraulic or mechanical machines designed to compress metal powders into precise shapes and densities. This process is a cornerstone of powder metallurgy (PM), a manufacturing technology that offers unique advantages in producing complex, high-performance parts with minimal material waste. The compaction press applies significant pressure to metal powder contained within a die, forcing the particles to bond and form a "green" part, which is then sintered to achieve its final strength and properties.
 A modern hydraulic powder metal compaction press, showing the die set, upper and lower punches, and control panel. The machine is designed for high-pressure application and precision shaping of metal powders.zzzz
A modern hydraulic powder metal compaction press, showing the die set, upper and lower punches, and control panel. The machine is designed for high-pressure application and precision shaping of metal powders.zzzz
How Does a Powder Metal Compaction Press Work?
The operation of a powder metal compaction press can be broken down into several critical stages, each essential for producing a uniform and robust green part.
1. Powder Filling
The process begins with the automatic filling of the die cavity with a precise amount of metal powder. The powder blend typically includes base metal powders, alloying elements, and a lubricant to facilitate compaction and ejection.
2. Compaction
Once the die is filled, the upper and lower punches move to apply pressure. The pressure range can vary dramatically, from 10 tons per square inch (tsi) for softer materials like bronze to over 50 tsi for iron-based alloys. This high pressure causes the powder particles to deform, fracture, and interlock, creating a coherent but fragile green part.
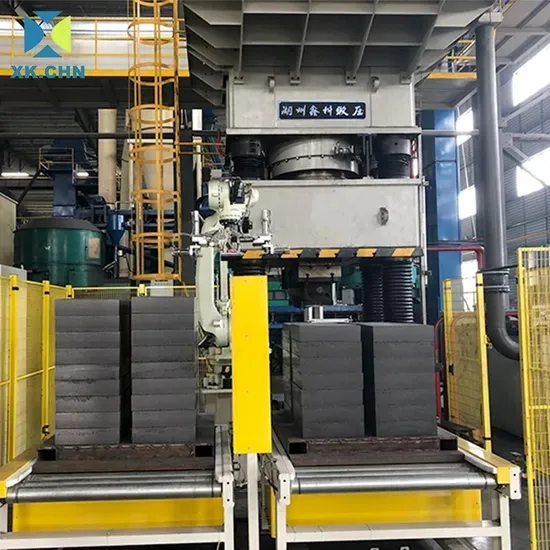
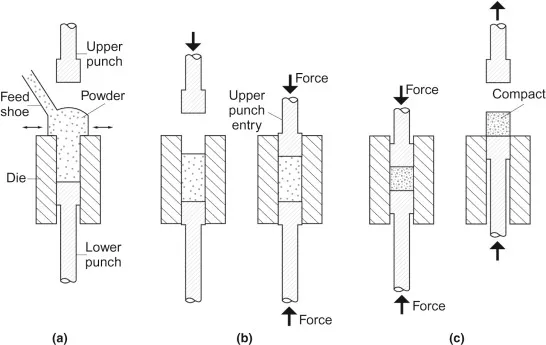 A schematic diagram showing the sequential steps of the powder compaction process: powder filling, compaction by upper and lower punches, and ejection of the green part.zzzz
A schematic diagram showing the sequential steps of the powder compaction process: powder filling, compaction by upper and lower punches, and ejection of the green part.zzzz
3. Ejection
After compaction, the upper punch retracts, and the lower punch pushes the finished green compact out of the die. This step requires precise control to avoid damaging the fragile part.
Types of Powder Metal Compaction Presses
There are two primary types of presses used in powder metallurgy, each with its own set of advantages and ideal applications.
Mechanical Presses
Mechanical presses use an eccentric drive or toggle mechanism to convert the rotary motion of a motor into the linear motion of the punches. They are known for their high speed and efficiency, making them ideal for high-volume production of simpler parts.
Advantages: High production speed, consistent cycle times, energy efficient for large runs.
Disadvantages: Limited flexibility in pressing complexity, fixed force curve.
Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic presses use fluid pressure to actuate the punches. They offer superior control over the pressing force and speed throughout the compaction cycle.
Advantages: Greater flexibility, higher and more controllable pressing forces, ability to produce complex, multi-level parts.
Disadvantages: Generally slower than mechanical presses, higher initial cost.
 A side-by-side comparison of the internal mechanisms of a mechanical press (left) and a hydraulic press (right), highlighting their different drive systems.zzzz
A side-by-side comparison of the internal mechanisms of a mechanical press (left) and a hydraulic press (right), highlighting their different drive systems.zzzz
Key Components of a Compaction Press
Understanding the major components helps in appreciating the precision of these machines.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Frame | Provides the rigid structure to withstand the high compaction forces without excessive deflection. |
| Die Set | The tooling that defines the shape of the part. It consists of a die and upper/lower punches. |
| Punch Actuation System | The mechanism (mechanical or hydraulic) that drives the punches to apply pressure. |
| Powder Feed System | Automatically meters and delivers the correct amount of powder into the die cavity. |
| Control System | A programmable logic controller (PLC) that manages the entire cycle, ensuring repeatability and precision. |
Advantages of the Powder Compaction Process
The use of powder metal compaction presses offers numerous benefits over traditional manufacturing methods like machining or casting.
- High Material Utilization: Near-net-shape production minimizes scrap, often achieving 97% material usage.
- Complex Geometries: Capable of producing intricate shapes with multiple levels and fine details that are difficult to machine.
- Mass Production & Consistency: Ideal for high-volume manufacturing with excellent part-to-part consistency.
- Controlled Porosity: Allows for the creation of self-lubricating bearings or filters by controlling density.
- Wide Material Choice: Can process a vast range of materials, including iron, steel, stainless steel, copper, and tungsten.
Applications of Compacted Powder Metal Parts
Parts produced by powder metal compaction presses are ubiquitous in modern industry.
| Industry | Application Examples |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine connecting rods, transmission gears, oil pump gears, valve guides, shock absorber parts. |
| Aerospace | Turbine engine components, heat shields, brake pads. |
| Consumer Appliances | Gears in power tools, locks, and washing machines. |
| Medical | Porous implants, surgical instrument components. |
| Industrial | Bearings, bushings, electrical contacts. |
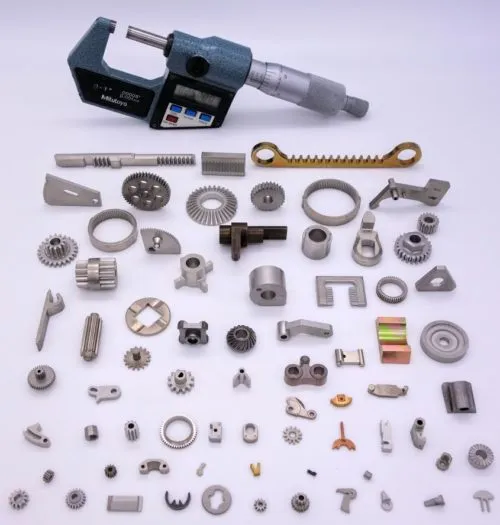 An assortment of finished sintered powder metal parts, showcasing complex gears, sprockets, and structural components used in various industries.zzzz
An assortment of finished sintered powder metal parts, showcasing complex gears, sprockets, and structural components used in various industries.zzzz
Conclusion
The powder metal compaction press is an indispensable piece of technology in advanced manufacturing. Its ability to transform metal powder into precise, high-strength, and complex components efficiently and with minimal waste solidifies its role as a critical enabler for industries ranging from automotive to aerospace. Continued advancements in press control, tooling design, and powder materials promise to further expand the capabilities and applications of this vital manufacturing process.