Progressive Die Stamping: The Complete Guide to High-Volume Metal Forming
Progressive die stamping represents one of the most efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes for producing high-volume metal components. This advanced metal forming technique has transformed industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and consumer goods by enabling the mass production of complex parts with exceptional precision and repeatability.
What is Progressive Die Stamping?
Progressive die stamping is a metalworking process that utilizes a series of stamping stations arranged in progression within a single die set. As a metal strip feeds through the stamping press, each station performs a specific operation—such as punching, bending, coining, or drawing—until the final part is completed and separated from the strip.
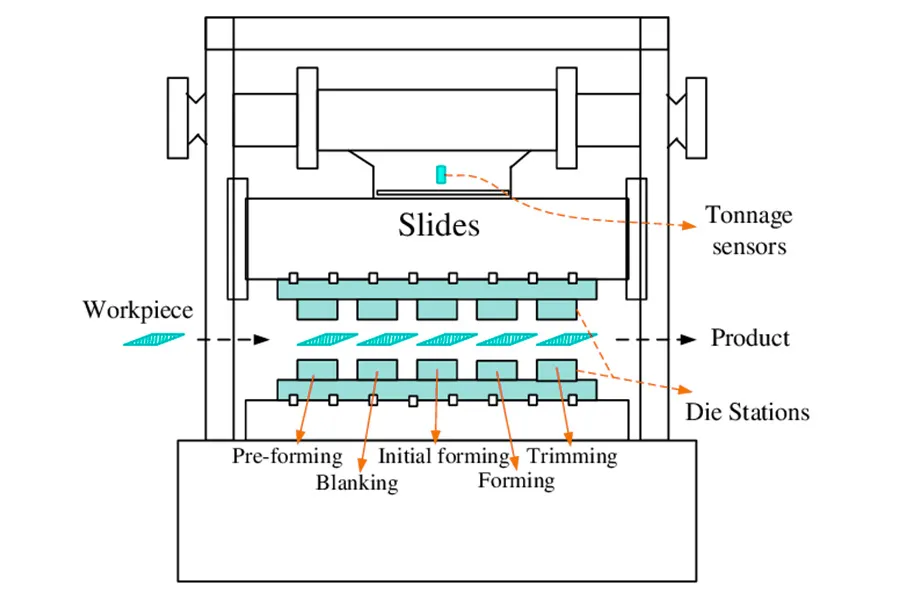
Key Components of Progressive Die Stamping Systems
The Progressive Die
The progressive die is the heart of the stamping system, consisting of multiple stations that perform sequential operations. Each station is precisely engineered to transform the metal strip gradually into the finished product.
Stamping Press
Stamping presses provide the necessary force and motion to drive the die. These machines range from mechanical to hydraulic systems, with tonnage capacities tailored to specific application requirements.
Feeding Mechanism
Automated feeding systems precisely advance the metal strip through the die at high speeds, ensuring consistent positioning for each stamping operation.

The Progressive Die Stamping Process Step by Step
The progressive die stamping process follows a carefully orchestrated sequence:
- Material Loading: Coiled metal stock is loaded into the feeding system
- Strip Feeding: The material advances through the die at precise intervals
- Piloting: Pilot pins ensure accurate strip positioning
- Stamping Operations: Multiple operations occur simultaneously at different stations
- Part Separation: Finished parts are separated from the carrier strip
- Scrap Removal: Remaining skeleton material is collected for recycling
Advantages of Progressive Die Stamping
| Advantage | Description | Impact on Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| High Production Rates | Capable of producing thousands of parts per hour | Significantly reduces per-part cost and increases output |
| Exceptional Precision | Tight tolerances maintained throughout production run | Ensures consistent part quality and reduces rejects |
| Reduced Labor Costs | Highly automated process requiring minimal operator intervention | Lowers overall manufacturing expenses |
| Material Efficiency | Optimized nesting reduces material waste | Minimizes raw material costs and environmental impact |
| Complex Part Capability | Ability to produce intricate geometries in single operation | Eliminates secondary operations and handling |
Applications Across Industries
Automotive Industry
Progressive die stamping produces critical automotive components including brackets, connectors, electrical contacts, and structural elements. The automotive sector relies heavily on this process for its ability to maintain consistent quality across high-volume production runs.
Electronics and Electrical Components
The electronics industry utilizes progressive die stamping for manufacturing connectors, lead frames, shielding components, and various precision parts requiring tight tolerances and high conductivity.
Consumer Goods
From appliance components to hardware fixtures, progressive die stamping enables cost-effective production of consumer products while maintaining aesthetic and functional requirements.

Design Considerations for Progressive Die Stamping
Successful progressive die stamping requires careful consideration of several design factors:
| Design Factor | Consideration | Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Formability, strength, and thickness consistency | Choose materials with consistent mechanical properties |
| Part Geometry | Complexity, bend radii, and feature spacing | Design for manufacturability with adequate clearances |
| Tolerance Requirements | Critical dimensions and allowable variations | Specify realistic tolerances based on material capabilities |
| Strip Layout | Material utilization and feeding stability | Optimize nesting to minimize waste and ensure smooth feeding |
| Tooling Access | Space for punches, dies, and sensors | Ensure adequate clearance for maintenance and monitoring |
Recent Technological Advancements
Digitalization and Industry 4.0
Modern progressive die stamping facilities are embracing digital transformation through IoT sensors, real-time monitoring systems, and predictive maintenance algorithms that optimize production efficiency and reduce downtime.
Advanced Tooling Materials
The development of premium tool steels, carbide inserts, and specialized coatings has extended tool life and improved stamping performance, particularly when working with advanced high-strength materials.
Precision Sensing and Control
Advanced vision systems, laser measurement, and in-process monitoring technologies ensure consistent quality control throughout high-speed production runs.

Economic Considerations and ROI
While progressive die stamping requires significant initial investment in tooling and equipment, the long-term economic benefits are substantial. The high production speeds, reduced labor requirements, and material efficiency typically result in excellent return on investment for high-volume applications. Production volumes of 50,000 parts or more generally justify the tooling costs, with per-part costs decreasing significantly as production quantities increase.
Future Trends in Progressive Die Stamping
The future of progressive die stamping is shaped by several emerging trends, including the integration of artificial intelligence for process optimization, the development of hybrid manufacturing systems combining additive and subtractive processes, and increased focus on sustainability through improved material utilization and energy efficiency. Additionally, the ability to process advanced materials, including composites and specialized alloys, continues to expand the applications for this versatile manufacturing technology.
Conclusion
Progressive die stamping remains a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness for high-volume metal component production. As technology continues to advance, this proven manufacturing method evolves to meet the increasingly demanding requirements of various industries while maintaining its position as one of the most reliable and economical metal forming processes available.