Spinning Machine for Yarn: The Heart of Textile Manufacturing
The spinning machine for yarn stands as one of the most pivotal inventions in industrial history, transforming raw fibers into continuous, strong, and uniform yarns that form the very foundation of the global textile industry. From the rudimentary spinning wheels of the past to today's fully automated, computer-controlled systems, the evolution of spinning machinery reflects a relentless pursuit of efficiency, quality, and versatility. This article delves into the core principles, types, technological advancements, and critical role of spinning machines in modern manufacturing.
Fundamental Principles of Yarn Spinning
At its essence, spinning is the process of twisting together drawn-out strands of fibers to form yarn. The primary objectives are to impart strength, ensure uniformity, and achieve the desired thickness (count) and character. The modern spinning machine automates three key stages: drafting, twisting, and winding. Drafting attenuates the fiber mass to the required fineness, twisting inserts the necessary cohesion, and winding packages the finished yarn onto bobbins or cones for subsequent use.
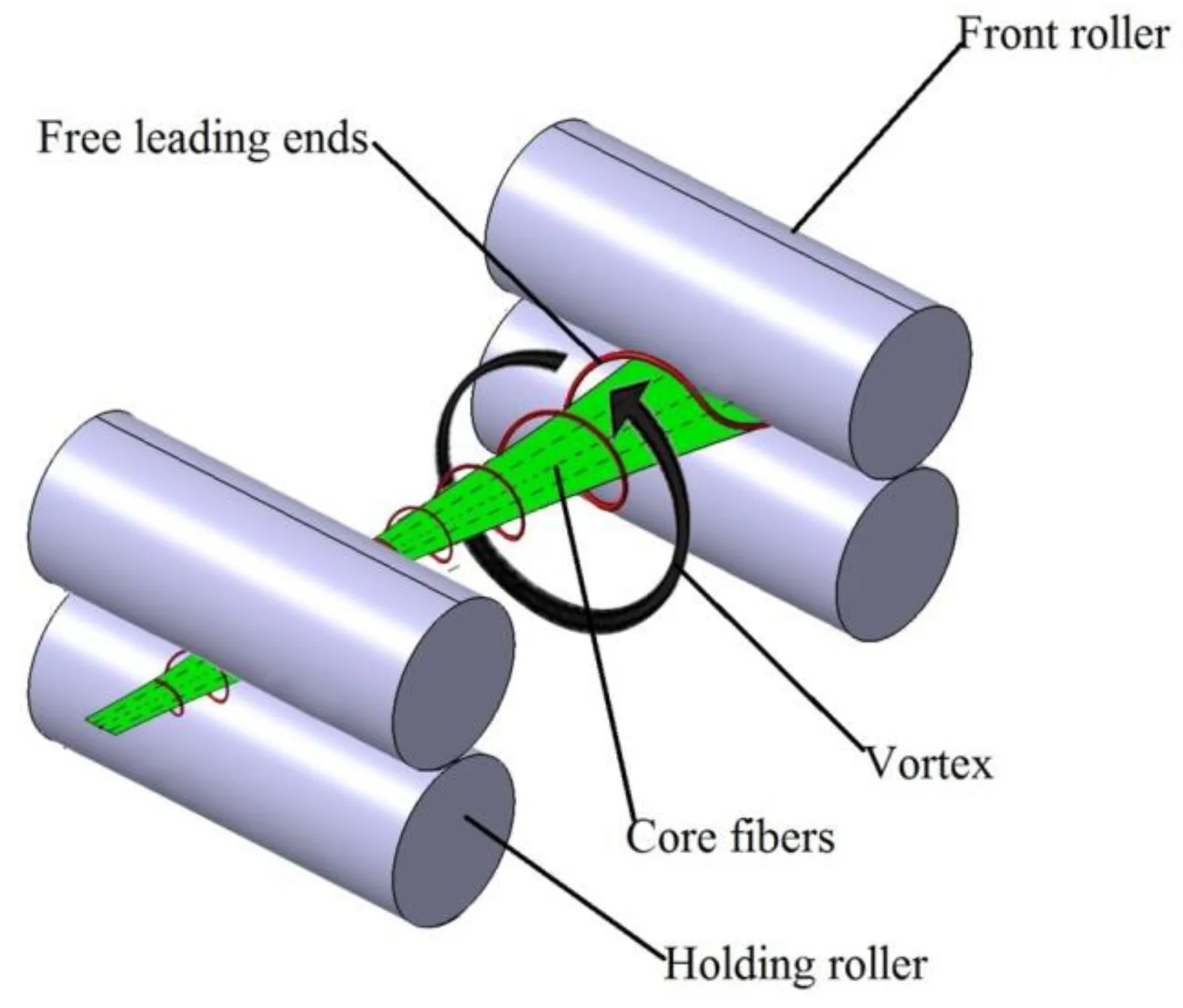
Figure 1: The spinning zone where fibers are drafted and twisted, forming the core of the yarn structure.
Major Types of Spinning Machines
Different spinning technologies have been developed to handle various fiber types and end-use requirements. The choice of machine significantly impacts the yarn's properties, production speed, and cost.
Ring Spinning
Ring spinning is the most widespread and versatile method, capable of producing high-quality, strong yarns from a wide range of fibers. It involves a spindle, a traveler, and a ring. The twisting and winding actions occur simultaneously, resulting in a dense, robust yarn. While it offers superior yarn quality, it is relatively slower compared to newer technologies.
Rotor Spinning (Open-End Spinning)
Rotor spinning, or open-end spinning, is a break-through technology that eliminates the need for roving and ring/traveler mechanisms. Fibers are individualized and deposited into a high-speed rotor where twist is inserted. This process is significantly faster than ring spinning and produces yarn with good uniformity, though it is typically less strong and hairier, making it ideal for denim, towels, and casual wear.
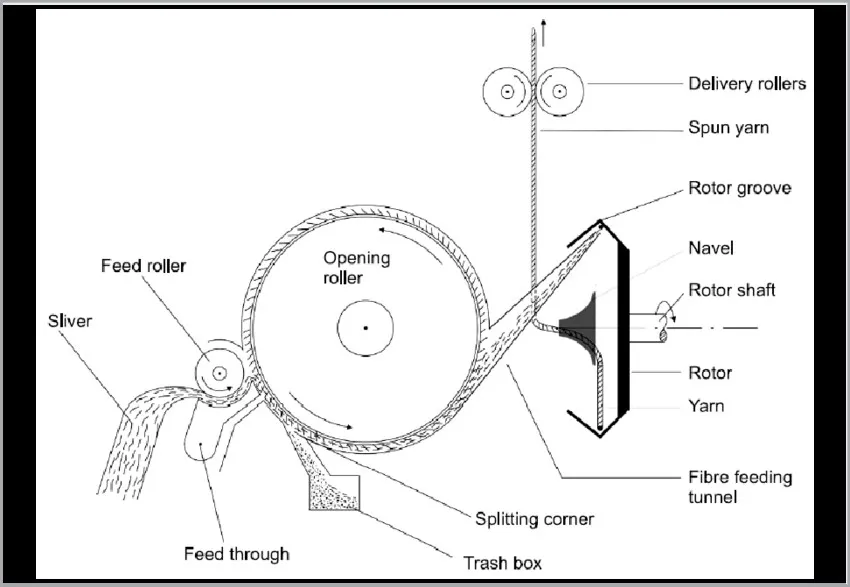
Figure 2: Schematic of the rotor spinning process, highlighting its high-speed, open-end principle.
Air-Jet Spinning
Air-jet spinning uses compressed air to twist fibers, creating a yarn structure where a core of parallel fibers is wrapped by surface fibers. It is an extremely high-speed process suitable for producing smooth yarns from synthetic blends and cotton, often used in shirting and bedding fabrics.
Technological Advancements and Automation
The modern spinning mill is a hub of digital integration and automation. Key advancements include:
- Automated Doffing and Piecing: Robots automatically remove full bobbins (doffing) and rejoin broken yarns (piecing), maximizing machine uptime.
- Integrated Monitoring Systems: Sensors continuously track yarn tension, evenness, and defects, feeding data to central control systems for real-time quality assurance.
- Energy-Efficient Drives: Modern machines utilize servo motors and frequency converters to reduce power consumption significantly.
- Digital Spinning Preparation: Blending, carding, and drawing processes are precisely controlled by computers to ensure optimal fiber preparation before spinning.
| Spinning Type | Typical Speed | Yarn Strength | Yarn Character | Primary Fiber Suitability | Common End Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ring Spinning | 15-25 m/min | Very High | Smooth, Dense | Cotton, Wool, Blends | Premium Apparel, Denim, Sewing Thread |
| Rotor Spinning | 120-250 m/min | Good | Bulky, Hairy | Cotton, Waste Fibers | Denim, Towels, Casual Knits |
| Air-Jet Spinning | 300-450 m/min | Moderate | Smooth, Less Hairy | Cotton, Synthetic Blends | Shirting, Bed Linens |
The Role in Sustainable Manufacturing
Contemporary spinning machines are designed with sustainability at the forefront. They minimize waste through precise material handling, reduce energy and water consumption, and enable the efficient processing of recycled fibers. The ability to produce consistent, high-quality yarn from post-consumer or pre-consumer waste is crucial for the circular textile economy.

Figure 3: A view of a highly automated and sustainable spinning mill utilizing advanced machinery.
Conclusion
The spinning machine for yarn is far more than just industrial equipment; it is a sophisticated engineering system that continuously adapts to the demands of fashion, performance, and sustainability. As technology progresses with trends like Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing, spinning machines will become even more intelligent, interconnected, and efficient, ensuring their central role in creating the fabrics that shape our world. From raw fiber to finished thread, these machines truly spin the threads of human innovation.