The Evolution of Progressive Die Press Technology
Historical Development of Progressive Die Presses
Early Mechanical Press Systems
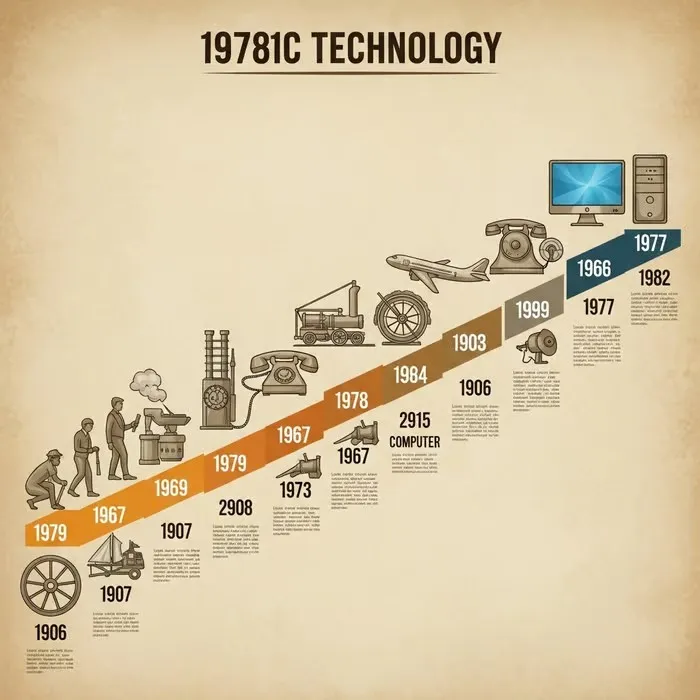
The origins of progressive die press technology date back to the early 20th century when manufacturers began developing mechanical press systems for mass production. These early systems were primarily mechanical, relying on flywheels and clutch mechanisms to generate stamping force. The first progressive die presses operated at relatively slow speeds, typically 50-100 strokes per minute, and required significant manual intervention for material feeding and part removal.
The Hydraulic Revolution
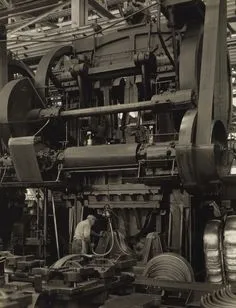
The introduction of hydraulic systems in the 1950s marked a significant advancement in progressive die press technology. Hydraulic presses offered superior control over force application and stroke length, enabling more complex forming operations. This period saw the development of more sophisticated die designs capable of performing multiple operations in a single press cycle, dramatically reducing production time and labor costs.
Modern Progressive Die Press Technology
Computer-Integrated Manufacturing Systems
The integration of computer numerical control (CNC) technology in the 1980s transformed progressive die presses into highly automated manufacturing systems. Modern presses feature sophisticated control systems that monitor and adjust parameters in real-time, ensuring consistent quality and reducing the risk of defects. The implementation of servo-driven technology has further enhanced precision while reducing energy consumption.

Advanced Material Handling Systems
Contemporary progressive die presses incorporate sophisticated material handling systems that automatically feed coil stock through the die stations. These systems include precision uncoilers, straighteners, and feed mechanisms that maintain exact material positioning throughout the stamping process. The development of quick-die-change systems has significantly reduced setup times, improving overall equipment effectiveness.
Key Technological Advancements
Precision Engineering and Tooling
The evolution of progressive die technology has been closely tied to advancements in tooling design and manufacturing. Modern progressive dies incorporate multiple stations, each performing specific operations such as piercing, blanking, bending, and forming. The use of carbide tooling and advanced coatings has extended tool life and improved performance in high-volume production environments.
| Generation | Period | Maximum Speed (SPM) | Control System | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Generation | 1920-1950 | 50-100 | Mechanical | Basic mechanical controls, manual feeding |
| Second Generation | 1950-1980 | 100-400 | Hydraulic | Improved force control, basic automation |
| Third Generation | 1980-2000 | 400-1200 | CNC | Computer control, enhanced precision |
| Fourth Generation | 2000-Present | 1200-2000+ | Servo & Smart Control | AI integration, IoT connectivity, predictive maintenance |
Digital Integration and Industry 4.0
The latest generation of progressive die presses embraces Industry 4.0 principles, incorporating IoT sensors, data analytics, and cloud connectivity. These smart presses collect and analyze performance data in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and optimizing production parameters. The integration of artificial intelligence algorithms allows for automatic adjustment of press settings based on material variations and environmental conditions.
Applications and Industry Impact
Automotive Manufacturing
Progressive die presses have become essential in automotive manufacturing, producing everything from simple brackets to complex structural components. The technology enables high-volume production of identical parts with tight tolerances, crucial for modern vehicle assembly. The automotive industry's shift toward lightweight materials has driven further innovation in progressive die technology.
Electronics and Consumer Goods
The electronics industry relies heavily on progressive die presses for manufacturing connectors, shielding components, and other precision parts. The ability to produce miniature components with extreme accuracy has made progressive die technology indispensable in consumer electronics manufacturing.
Future Trends and Developments
Additive Manufacturing Integration
The integration of additive manufacturing technologies with progressive die presses represents the next frontier in metal forming. Hybrid systems combining traditional stamping with 3D printing capabilities are emerging, enabling the production of components with previously impossible geometries and material combinations.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Future developments in progressive die press technology will focus increasingly on sustainability. This includes the development of energy-efficient servo motors, recycling systems for scrap material, and the use of environmentally friendly lubricants and coolants. The industry is also moving toward closed-loop systems that minimize waste and energy consumption.
| Technology Type | Energy Efficiency (%) | Setup Time (minutes) | Part-to-Part Variation (mm) | Maximum Production Rate (parts/hour) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Mechanical | 45-55 | 120-180 | ±0.1 | 3,000 |
| Hydraulic | 50-65 | 90-120 | ±0.05 | 6,000 |
| Servo-Electric | 75-85 | 30-60 | ±0.02 | 12,000 |
| Smart Servo (Current) | 85-95 | 10-20 | ±0.005 | 18,000+ |
Conclusion
The evolution of progressive die press technology represents a remarkable journey from basic mechanical systems to sophisticated, intelligent manufacturing platforms. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in precision, efficiency, and sustainability. The integration of digital technologies and the ongoing development of smart manufacturing systems will ensure that progressive die presses remain at the forefront of metal forming technology for years to come.