The Future of Metal Fabrication: High-Speed Stamping Press Innovations
The landscape of metal fabrication is being reshaped by a wave of technological advancements, with high-speed stamping presses at the forefront of this revolution. No longer just powerful machines for cutting and forming, modern stamping presses are integrated systems that combine speed with unprecedented levels of control, intelligence, and connectivity. This article explores the key innovations driving the future of this critical manufacturing process.
1. The Rise of Servo-Driven Presses: Unlocking Unprecedented Control
The most significant shift in recent years has been the widespread adoption of servo-motor technology, replacing traditional mechanical and hydraulic systems. Servo-driven presses utilize a high-torque servo motor to directly control the slide motion, breaking free from the fixed cycle of conventional presses.
Key Advantages of Servo Technology:
- Programmable Slide Motion: Operators can program the slide's path, velocity, and dwell times with extreme precision. This allows for optimized forming speeds for different materials and complex geometries, reducing stress and improving part quality.
- Enhanced Flexibility: A single servo press can mimic the motion profiles of multiple traditional presses, making it ideal for high-mix, low-volume production runs common in today's market.
- Energy Efficiency: Servo presses consume energy only when in motion, unlike hydraulic presses that run pumps continuously. This can lead to energy savings of 30% or more.
- Reduced Noise and Vibration: The controlled motion of servo presses results in significantly lower operational noise and vibration, contributing to a better working environment and reduced machine wear.
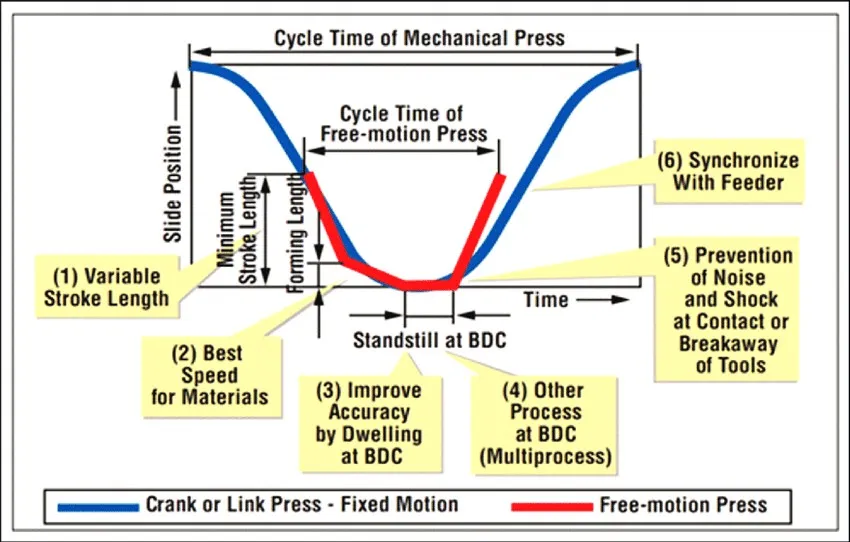 The flexibility of servo press motion profiles allows for "soft" touch feeding and optimized forming speeds.
The flexibility of servo press motion profiles allows for "soft" touch feeding and optimized forming speeds.
2. Digitalization and the Smart Stamping Cell
The high-speed stamping press is becoming the central node in a connected, data-rich smart manufacturing cell. The integration of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) sensors and sophisticated software is creating a new paradigm of predictive and proactive operation.
Core Elements of a Smart Stamping System:
| Component | Function | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| IIoT Sensors | Monitor tonnage, temperature, vibration, and energy consumption in real-time. | Enables condition monitoring and early detection of anomalies. |
| Cloud Platforms & AI Analytics | Aggregate and analyze machine data to identify patterns and predict failures. | Moves maintenance from reactive to predictive, minimizing unplanned downtime. |
| Digital Twins | A virtual replica of the press and die system used for simulation and optimization. | Allows for die tryout and process optimization in a virtual environment, reducing setup time and physical prototyping costs. |
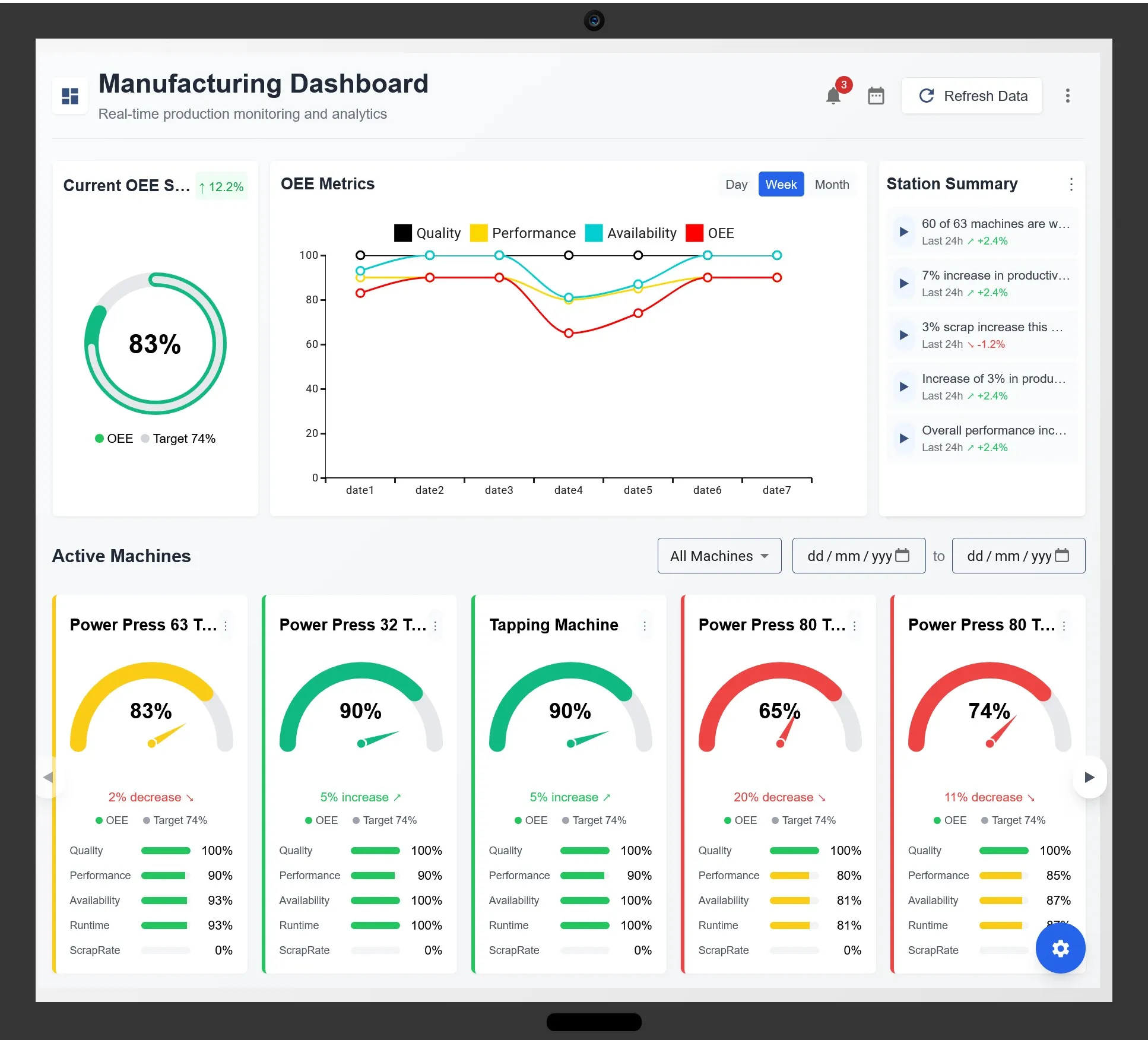 Real-time data dashboards provide operators with actionable insights for immediate process control.
Real-time data dashboards provide operators with actionable insights for immediate process control.
3. Advanced Tooling and Material Handling Innovations
The press itself is only part of the equation. To achieve true high-speed production, innovations in tooling and material feeding are equally critical.
Tooling Advancements:
The development of harder, more durable die materials, such as powdered metals and advanced coatings, significantly extends tool life in high-volume stamping. Furthermore, quick-die-change (QDC) systems, often automated, have revolutionized press productivity. These systems can reduce die changeover times from hours to minutes, making small batch production economically viable.
Automated Material Handling:
High-speed presses are increasingly paired with robotic arms or sophisticated destacker feeders for loading blanks and unloading finished parts. This not only maximizes speed but also ensures consistency and removes human operators from potentially hazardous tasks.
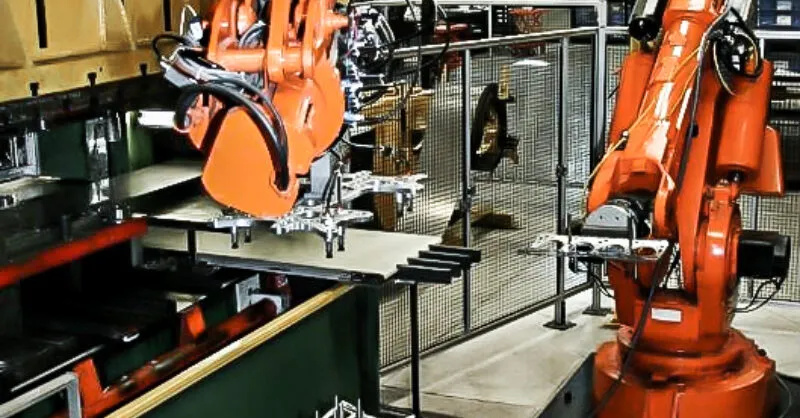 Robotic automation integrated with stamping presses ensures continuous, high-speed production with minimal human intervention.
Robotic automation integrated with stamping presses ensures continuous, high-speed production with minimal human intervention.
4. Meeting the Demands of New Materials and Industries
The push for lighter, stronger, and more sustainable products is driving the use of new materials, which in turn demands more from stamping technology.
- Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS): Common in the automotive industry for lightweighting, AHSS requires higher forming forces and more precise control to avoid springback and cracking. Servo presses are uniquely suited for this task.
- Electronics and Miniaturization: The trend towards smaller, more complex electronic components (e.g., connectors, shields) requires stamping presses capable of micron-level precision at very high speeds.
- Sustainable Practices: Innovations also focus on sustainability, such as presses designed for stamping recycled aluminum or for producing components for electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
Conclusion: An Integrated, Intelligent Future
The future of metal fabrication lies not in isolated machines, but in fully integrated, intelligent systems. The high-speed stamping press has evolved into a highly adaptable, data-driven manufacturing center. The convergence of servo technology, digitalization, and advanced automation is creating a new era of manufacturing characterized by unparalleled efficiency, flexibility, and quality. As these innovations continue to mature, they will empower manufacturers to meet the challenges of tomorrow's market with confidence and precision.