What is a Stamping Machine Used For? - Complete Guide
Stamping machines, also known as press machines or stamping presses, are fundamental manufacturing equipment used across numerous industries to transform flat metal sheets into specific shapes and components through various forming processes. These powerful machines apply tremendous force to metal workpieces using specialized tools and dies, enabling mass production of identical parts with exceptional precision and efficiency.
Primary Functions and Applications of Stamping Machines
Metal Forming and Shaping
The core function of stamping machines is to deform metal sheets into desired configurations. This process involves placing a flat metal sheet between two dies and applying compressive force to reshape the material. The applications range from simple brackets to complex automotive body panels.
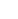
Punching and Piercing Operations
Stamping machines excel at creating holes, slots, and cutouts in metal sheets. The punching process involves a punch tool penetrating through the metal sheet into a matching die, shearing the material to create precise openings. This function is crucial for components requiring assembly points, ventilation, or weight reduction.
Blank Production
Before complex forming operations, stamping machines produce blanks - flat pieces of metal cut into specific shapes that serve as starting material for subsequent manufacturing processes. These blanks are precisely sized and shaped according to design specifications.
Types of Stamping Machines and Their Specific Uses
| Machine Type | Primary Function | Common Applications | Force Capacity Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Press | High-speed punching and blanking | Electronics components, small brackets | 5-3000 tons |
| Hydraulic Press | Deep drawing and complex forming | Automotive panels, kitchen sinks | 10-10,000 tons |
| Servo Press | Precision stamping with programmable control | Medical devices, aerospace components | 5-2000 tons |
| Progressive Die Press | Multiple operations in single machine cycle | Connectors, electrical contacts | 20-2000 tons |
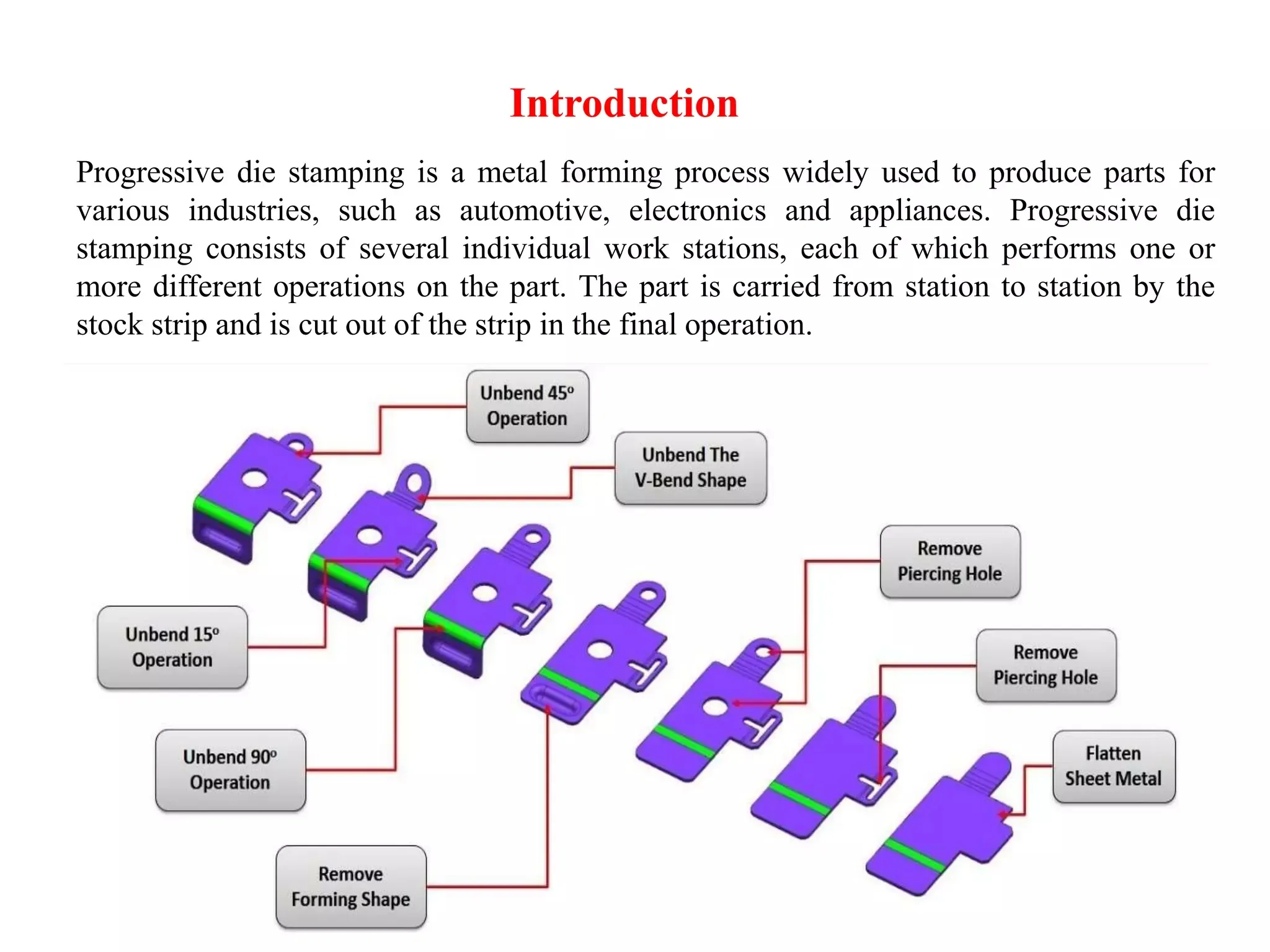
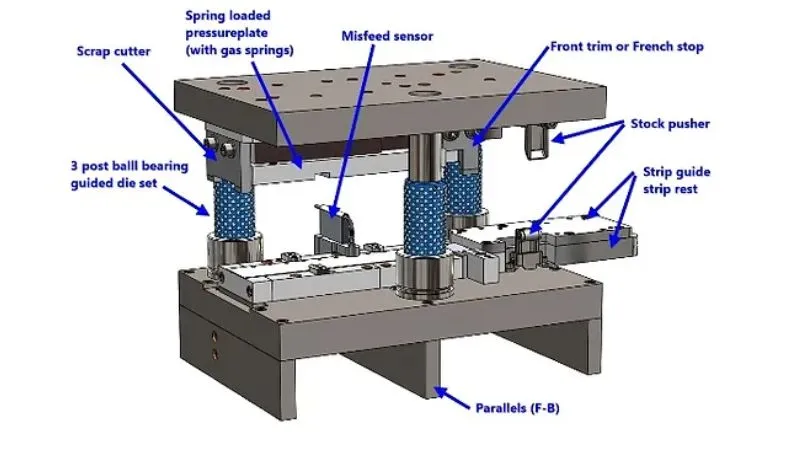
Key Industries Utilizing Stamping Machines
Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry represents the largest user of stamping technology. These machines produce body panels, chassis components, brackets, and structural elements. A single automobile contains hundreds of stamped parts, demonstrating the critical role of stamping in vehicle manufacturing.
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace applications, stamping machines create lightweight yet strong components for aircraft structures, engine parts, and defense equipment. The precision and repeatability of modern stamping presses meet the stringent quality requirements of this sector.
Electronics and Consumer Goods
Stamping machines manufacture enclosures, heat sinks, connectors, and shielding components for electronic devices. The ability to produce small, intricate parts with tight tolerances makes stamping indispensable for consumer electronics manufacturing.

Appliance Manufacturing
Home and industrial appliances rely heavily on stamped components. From refrigerator panels to washing machine drums, stamping machines produce the metal parts that form the structure and functionality of modern appliances.
Stamping Process Variations and Their Applications
| Process Type | Description | Typical Products | Material Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blanking | Cutting finished parts from sheet metal | Gaskets, washers, simple brackets | 0.1-6 mm |
| Embossing | Creating raised or recessed designs | Decorative panels, nameplates | 0.2-3 mm |
| Coining | High-pressure compression for fine details | Coins, medals, precision parts | 0.5-10 mm |
| Flanging | Creating flanges or rims on parts | Pipe fittings, container ends | 0.5-8 mm |
Advantages of Modern Stamping Technology
High Production Efficiency
Modern stamping machines can produce hundreds or thousands of parts per hour, significantly outperforming manual fabrication methods. This high throughput makes stamping ideal for mass production environments.
Exceptional Precision and Consistency
Computer-controlled stamping presses maintain tight tolerances, often within ±0.01 inches, ensuring every produced part matches design specifications exactly. This consistency reduces assembly issues and improves final product quality.
Material Utilization and Cost Effectiveness
Advanced nesting software optimizes material usage, minimizing waste. The combination of high-speed production and efficient material use results in lower per-part costs, especially for high-volume manufacturing.

Future Trends in Stamping Machine Technology
The evolution of stamping technology continues with advancements in servo motor technology, intelligent control systems, and integration with Industry 4.0 principles. Smart stamping machines now feature real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance capabilities, and seamless data integration with factory management systems. These developments further enhance productivity, quality control, and operational efficiency in modern manufacturing environments.
As materials science advances and demand for lightweight, high-strength components grows, stamping machines will continue to adapt, incorporating new capabilities for processing advanced alloys, composites, and specialized materials to meet the evolving needs of global manufacturing.